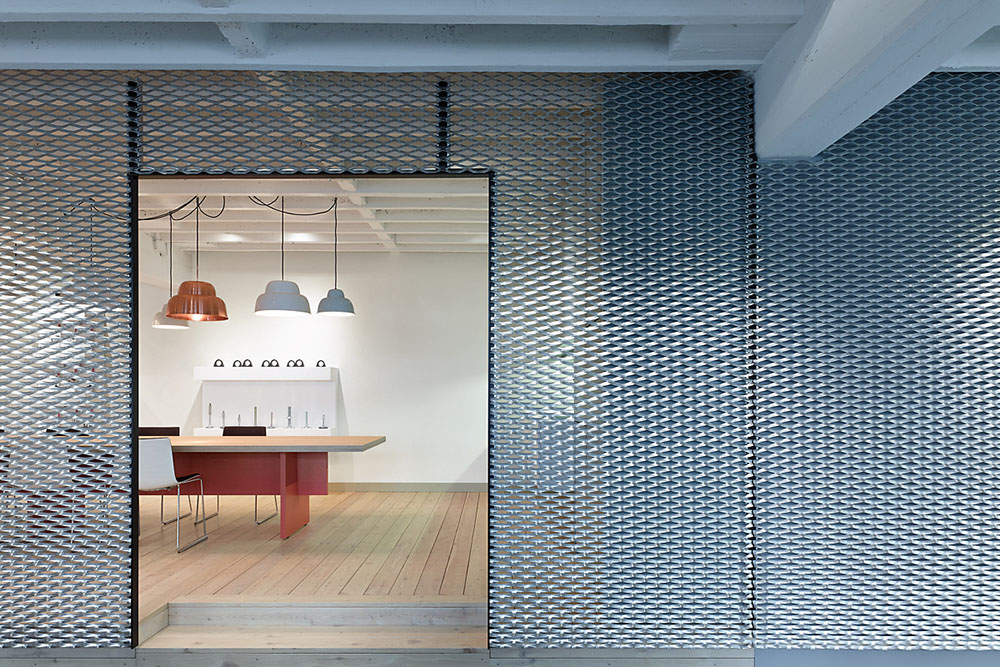
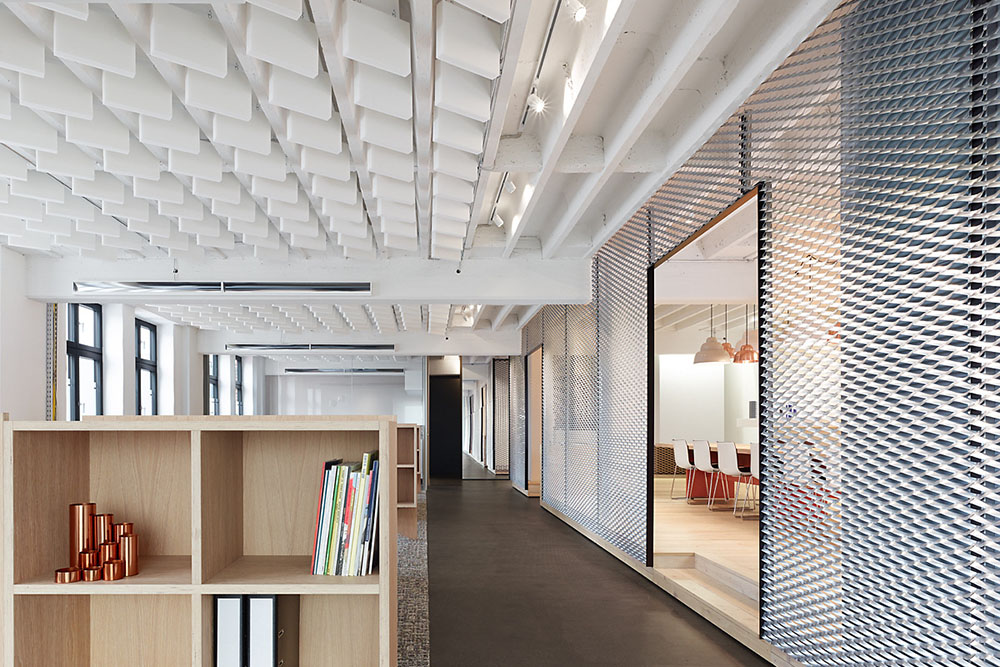
The galvanized expanded metal is a versatile and high-performance material widely used in construction, architecture, and industrial fields. Manufactured from low-carbon steel through punching and stretching, it forms a continuous mesh structure—typically diamond or hexagonal in shape—before being coated with zinc via hot-dip or electro-galvanizing. This zinc coating serves as both a physical barrier and an electrochemical protector, dramatically improving corrosion resistance while retaining the metal’s inherent strength and flexibility.
1. Advantages and Disadvantages of Galvanized Expanded Metal
Advantages
1. Excellent Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Hot-dip galvanized expanded metal typically features a zinc coating of up to 12 microns, while electro-galvanized coatings measure around 5 microns. This dense protective layer enables the material to pass a 96-hour salt spray test without rusting—equivalent to a lifespan of more than 10 years under normal environmental conditions. Compared with untreated steel, its corrosion resistance is 3–5 times higher, making it ideal for use in humid, acidic, or alkaline environments.
2. High Strength and Lightweight Structure
The low-carbon steel base provides high tensile strength and exceptional load-bearing capacity. Because the mesh is formed in a single expansion process without welding, it maintains excellent structural integrity. Additionally, this process reduces the panel’s weight by up to one-third, making transportation and installation easier while reducing overall construction loads.
3. Versatile Design Advantages
The open mesh design allows for 40–70% air permeability, ensuring good ventilation and natural lighting. The diamond-shaped pattern also enhances anti-slip performance and water drainage, making it suitable for walkways, platforms, and outdoor decks. Furthermore, its non-combustible nature provides excellent fire and heat resistance.
Disadvantages
Despite its many strengths, galvanized expanded metal has a few limitations. The exposed edges after cutting or welding may corrode if not properly recoated with zinc. Additionally, its geometric mesh design limits the ability to create complex artistic patterns. Lastly, while it offers strong lifecycle value, its cost is slightly higher than that of ordinary wire mesh or plastic grating.
2. Core Applications in Building Exterior Walls
2.1 Reinforcement Layer for Exterior Wall Insulation Systems
When used as the reinforcing framework in exterior wall insulation systems, galvanized expanded metal provides exceptional crack resistance and structural stability. Its tensile strength allows it to bond firmly with insulation materials, forming a protective mortar layer that prevents cracking and water seepage.
Comparison of Alternatives:
-
Ordinary Welded Wire Mesh: Prone to rust; corrosion expansion may damage the mortar layer.
-
Fiberglass Mesh: Corrosion-resistant but low in strength, prone to fatigue fractures.
Conclusion: For high-rise and commercial building insulation systems, galvanized expanded metal offers unmatched durability and structural performance.
2.2 Exterior Wall Decoration and Sunshade Systems
As a decorative element or sunshade, galvanized expanded metal enhances both functionality and aesthetics. By adjusting porosity, designers can control shading coefficients (30–70%), reducing solar heat gain and improving building energy efficiency. Its metallic texture and reflective qualities create a modern architectural aesthetic.
Comparison of Alternatives:
-
Aluminum Alloy Grilles: Lightweight but costly and prone to deformation.
-
Fiber Composite Panels: Good corrosion resistance but poor fire performance.
Conclusion: For ventilation, shading, and fire-safe facade systems, galvanized expanded metal provides the best balance of strength, appearance, and cost-efficiency.
2.3 Scaffolding and Safety Netting
In construction sites, galvanized expanded metal serves as a robust and safe alternative to plastic safety netting. Its high load-bearing capacity and impact resistance ensure worker safety while maintaining adequate light and air circulation.
Comparison of Alternatives:
-
Plastic Mesh: Flammable and prone to aging.
-
Ordinary Expanded Steel (Ungalvanized): Rusts easily, leading to high replacement costs.
Conclusion: For large-scale, standardized construction projects, galvanized expanded metal scaffolding offers superior safety and long-term savings.
3. Comprehensive Comparison with Other Exterior Wall Materials
| Features | HIGHTOP Galvanized Expanded Steel | Stainless Steel Expanded Steel | Aluminum Perforated Panels | Ordinary Welded Wire Mesh |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (10+ years hot-dip zinc layer) | Excellent but high cost | Moderate, vulnerable in alkaline environments | Poor, frequent maintenance required |
| Strength / Load-bearing | High tensile strength | Very high but overengineered | Low, prone to deformation | Medium, weld cracking possible |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Best balance of cost and durability | 2–3× higher cost | Medium-high | Low initial cost, high maintenance |
| Fire Rating | Class A, non-combustible | Class A, non-combustible | Low melting point | Flammable |
| Ease of Installation | Lightweight and modular | Heavy, difficult to process | Lightweight but weak | Poor flexibility |
4. Why Choose HIGHTOP Galvanized Expanded Metal
1. Precise Coating Control:
HIGHTOP employs advanced hot-dip galvanizing technology to ensure a uniform zinc layer (≥12μm), providing long-term outdoor corrosion protection exceeding 10 years.
2. Customized Design Flexibility:
We offer various mesh patterns—diamond, hexagonal, and round—with thicknesses from 1mm to 8mm. Custom sizing and modular cutting options allow seamless integration into your design.
3. Lifecycle Cost Advantage:
While the unit cost is 20% higher than standard wire mesh, its maintenance-free lifespan reduces total ownership costs by up to 50%.
4. Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility:
The material is fully recyclable and produced using environmentally compliant processes, supporting green building certifications.
Conclusion
The galvanized expanded metal is more than just a protective layer—it is a durable, aesthetic, and cost-effective material that enhances the safety and performance of modern architecture. Whether used in facade systems, insulation reinforcements, or scaffolding safety structures, it delivers the ideal balance of strength, longevity, and design flexibility. With HIGHTTOP’s advanced production technology and customization capabilities, your project gains a partner dedicated to quality, sustainability, and long-term value.
Get in Touch
Please Email us via the contact form below, we will get back to you ASAP.